Bitcoin gave the same hype to Blockchain as ChatGPT for AI-ML. The Machine Learning Model has taken the technology sector and internet audiences by storm and is one of the most trending articles in recent times . Almost a decade back, Blockchain technology enjoyed the same popularity and undivided attention from investors and technologists alike. Even though its not mainstream yet, it had made waves of advancement since it was first announced. Its use cases span across many industries and there are some profound challenges which we could not solve before this technology was available for us. In this article lets dig a deeper into why Blockchain is not widely adopted yet and what are the emerging mechanisms to be considered.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a secure database shared across a network of participants, where up-to-date information is available to all participants at the same time.
In layman terms “Blockchain allows for the permanent, immutable, and transparent recording of data and transactions.”
A product/solution built on Blockchain Technology exhibits 3 main characteristics
- The database storing the transactions must be cryptographically secure. It means that there should be a private and public key to access or modify the data.
- The database is available online through public/private network.
- And lastly, the database is shared across the network for someone to add themselves to the network and become a node.
Enterprise Blockchain Adoption:
Blockchain technology has found applications in various industries, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, voting systems, real estate, and more.

However, like any technology, it also has its challenges, such as scalability, energy consumption (in some implementations, like PoW), and regulatory concerns in certain jurisdictions.
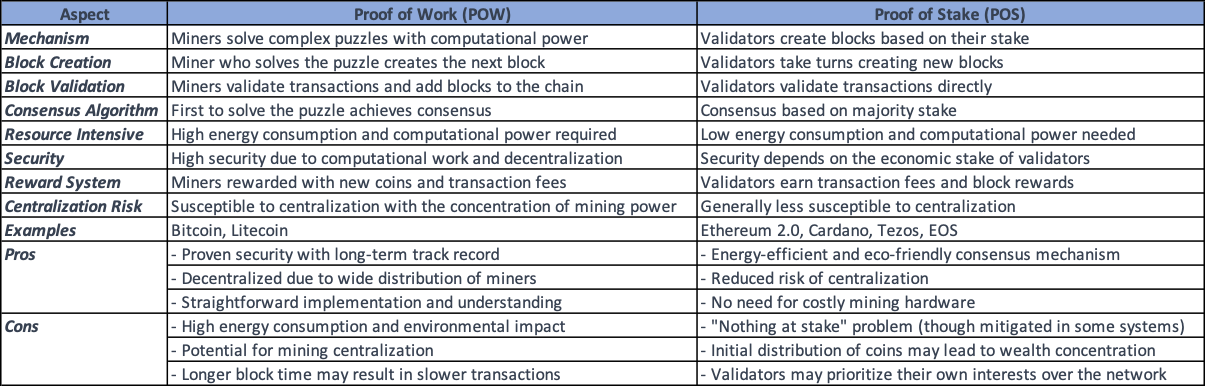
Blockchain energy consumption has been a prominent concern associated with Proof of Work (POW) consensus mechanisms used by certain blockchain networks, particularly those modeled after Bitcoin. To provide a perspective, the University of Cambridge estimates that Bitcoin — which uses proof of work for mining — consumes about .39% of the world’s annual electricity. Bitcoin mining uses more electricity annually than the countries of Finland and Belgium. On the other hand, Proof of Stake (POS) is one of the sustainable alternate to POW mechanism which will use 99.95% less energy according to Ethereum Foundation. POW relies on miners solving complex mathematical puzzles with computational power to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain. POS, on the other hand, allows validators to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. Below are some of the high level differences between POW and POS. Note that the in POS mechanism, the risk comes in the form of validators prioritizing their own interests by contributing higher stakes.
However, researchers and developers continue to work on improving the technology to address these limitations and explore new use cases. Lets hope that in the future there are more sustainable solutions with low risk which we can adapt and use this wonderful technology. In the mean time, here are some additional trends that are worth keeping an eye on:
- The development of quantum-resistant blockchains: Quantum computers pose a potential threat to blockchain security, as they could be used to break the cryptographic algorithms that protect blockchain networks. However, there is a lot of research being done on quantum-resistant blockchains, and it is likely that these will become available in the years to come.
- The convergence of blockchain with other technologies: Blockchain is being combined with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), to create new and innovative applications. This trend is expected to continue in the years to come, as blockchain becomes more widely integrated with other technologies.
- The growth of the decentralized web: The decentralized web is a new vision for the internet that is based on blockchain technology. In the decentralized web, users would have more control over their data and privacy, and they would be able to interact with each other without the need for intermediaries. This trend is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we use the internet.

